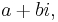Order (ring theory)
In mathematics, an order in the sense of ring theory is a subring 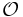 of a ring
of a ring 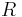 that satisfies the conditions
that satisfies the conditions
- R is a ring which is a finite-dimensional algebra over the rational number field
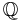
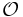 spans R over
spans R over 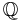 , so that
, so that 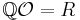 , and
, and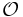 is a lattice in R.
is a lattice in R.
The third condition can be stated more accurately, in terms of the extension of scalars of R to the real numbers, embedding R in a real vector space (equivalently, taking the tensor product over 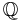 ). In less formal terms, additively
). In less formal terms, additively 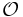 should be a free abelian group generated by a basis for R over
should be a free abelian group generated by a basis for R over 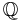 .
.
The leading example is the case where R is a number field K and 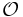 is its ring of integers. In algebraic number theory there are examples for any K other than the rational field of proper subrings of the ring of integers that are also orders. For example in the Gaussian integers we can take the subring of the
is its ring of integers. In algebraic number theory there are examples for any K other than the rational field of proper subrings of the ring of integers that are also orders. For example in the Gaussian integers we can take the subring of the
for which b is an even number. A basic result on orders states that the ring of integers in K is the unique maximal order: all other orders in K are contained in it.
When R is not a commutative ring, the idea of order is still important, but the phenomena are different. For example, the Hurwitz quaternions are a maximal order in the quaternions with rational co-ordinates; they are not the quaternions with integer coordinates in the most obvious sense. Maximal orders exist in general, but need not be maximum orders: there is in general no largest order, but a number of maximal orders. An important class of examples is that of integral group rings.
Because there is a local-global principle for lattices the maximal order question can be examined at a local field level. This technique is applied in algebraic number theory and modular representation theory.
Definition
An order 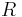 in a number field
in a number field 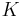 is a subring of
is a subring of 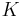 which as a
which as a 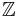 -module is finitely generated and of maximal rank
-module is finitely generated and of maximal rank 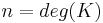 (note that we use the "modern" definition of a ring, which includes the existence of the multiplicative identity
(note that we use the "modern" definition of a ring, which includes the existence of the multiplicative identity  ).[1]
).[1]
References
- ^ Henri Cohen, A Course in Computational Algebraic Number Theory 3rd corrected printing, pp. 181, 1996, Springer
See also
- Hurwitz quaternion order - An example of ring order